Contact us today for a consultation with one of our physicians.
In the past, a stem cell transplant was more commonly called a bone marrow transplant because the stem cells were collected from the bone marrow. Now the stem cells are collected from the blood and not the bone marrow, therefore called stem cell transplant.
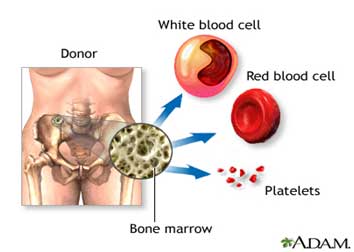
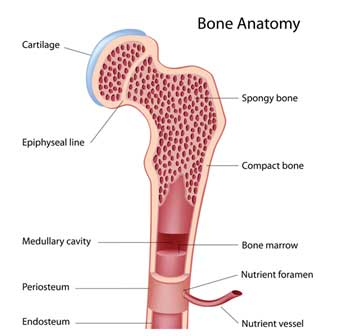
Bone marrow is the soft spongy tissue found inside the bones. The bone marrow makes blood cells and it contains cells called “hematopoietic” stem cells. These cells can turn into several other types of cells. They can turn into more bone marrow cells, or they can turn into any type of blood cell.
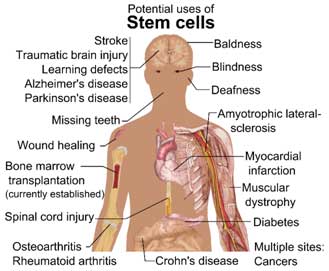
Bone marrow transplants are used as a treatment for some types of cancers. Bone marrow transplants are performed if you have leukemia, certain types of lymphoma, multiple myeloma and to treat certain blood diseases. There are certain types of cancers and other diseases that keep hematopoietic stem cells from developing normally, if they are not normal, neither are the blood cells that they make. A stem cell transplant provides new stem cells, and these new stem cells make new, healthy blood cells.
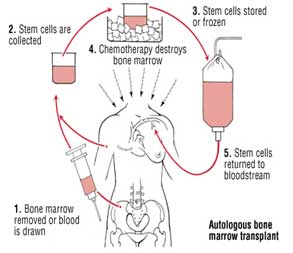
This is also called an AUTO transplant. In an AUTO transplant, you get your own stem cells after doctors treat the cancer. The process is as followed: First, the stem cells from your blood are collected and are froze. Second, powerful chemotherapy and or radiation therapy is done. Third, they thaw your frozen stem cells and lastly, they are placed back in your blood through an intravenous (IV) placed in your vein.
It takes about 24 hours for your stem cells to reach the bone marrow. Then they start to grow, multiply, and help the marrow make healthy blood cells again.
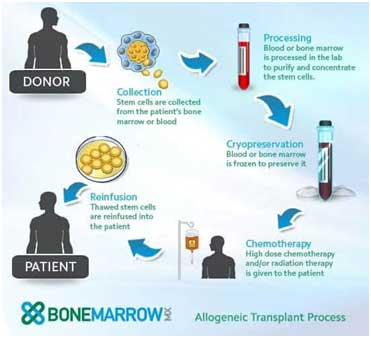
This is also called an ALLO transplant. In an ALLO transplant, you get another person’s stem cells. With the ALLO transplant it is very important to make sure the donors bone marrow matches yours. The reason for this, is because everyone has certain proteins in their white blood cells (WBC’s) called human leukocyte antigens (HLA). Matching proteins makes graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) less likely where healthy cells from the transplant attack your cells.
Once you find a donor, you receive chemotherapy with or without radiation therapy. Next, you get the other person’s stem cells through a tube placed in a vein (IV). The cells in an ALLO transplant are not typically frozen. This way, your doctor can give you the cells as soon as possible after chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Stem cells are cells from which all other cells with specialized functions are generated. Under the right conditions in the body or a laboratory, stem cells divide to form more cells called daughter cells. Daughter cells either become new stem cells (self-renewal) or specialized cells (differentiation) with a more specific function, such as blood cells, brain cells, heart muscle cells or bone cells. No other cell in the body has the natural ability to generate new cell types.
There are several different stem cells:
Embryonic stem cells come from embryos that are three to five days old. At this stage, an embryo is called a blastocyst and has about 150 cells. These stem cells can divide into more stem cells or can become any type of cell in the body. This changeability allows embryonic stem cells to be used to regenerate or repair diseased tissue and organs.
Adult stem cells are found in small numbers in bone marrow or fat. Compared with embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells have a more limited ability to give rise to various cells of the body. Adult stem cells may be able to create various types of cells, they may be able to create bone or heart muscle cells. Adult stem cells are currently being tested in people with neurological or heart disease.
Since 1988, Cord blood transplant has been around used in treating many disorders and critical diseases. Many doctors assure that cord blood makes a better alternative to bone marrow for patients, who require a stem cell transplant. There are some options:
Both cord blood and bone marrow transplants are conducted to replace the unhealthy cells with new and healthy cells. Umbilical cord blood is the source of cord blood stem cells while bone marrow is the source of bone marrow stem cells.
Cord blood is collected from the umbilical cord after a baby is born and it can be preserved for years. Cord blood stem cells have a more regenerative potential than bone marrow stem cells. These stem cells can be used to treat many diseases within the close family of the child. Doctors prefer cord blood stem cells, because of the richness source of stem cells found in the umbilical cord compared to bone marrow. Core blood transplants is a better option for people under the age of 30 and weigh less than 60kg. It is an ideal procedure for patients with lung, liver, kidney or hear problems, where Bone Marrow transplant is not recommended at all.
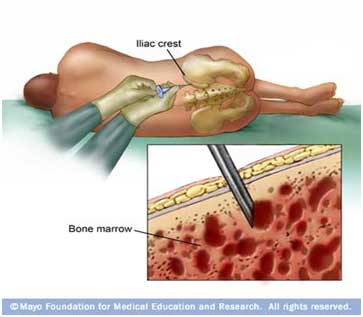
Bone marrow stem cells are collected from a matching donor. The marrow is usually extracted from the ribs, hips, skull, breastbone or spine. After the Stem cells are extracted, they are injected into the affected area of the patient immediately or can also be preserved for later use.
For more information about the Bone Marrow and Stem Cell Transplant procedures available to residents of Los Angeles and Beverly Hills, CA, please contact us at 855-SOMA-844 (855-766-2844).